Threat Intelligence is the process of gathering, analyzing, and applying knowledge about potential or existing cyber threats. It provides context around attacker behavior, motivations, and indicators of compromise (IOCs), helping organizations make informed decisions to secure their digital assets.
According to Gartner, threat intelligence delivers evidence-based insights and actionable advice on threats, enabling proactive cybersecurity measures.
Why Threat Intelligence Matters
Cyber attackers have become more agile, leveraging automation, AI, and sophisticated social engineering tactics. These advancements have resulted in more frequent, targeted, and stealthy attacks across all industries.
Threat Intelligence gives businesses the upper hand by:
Identifying and mitigating risks proactively: Organizations can preemptively detect threats based on real-time indicators and patterns, allowing them to strengthen defenses before an attack occurs.
Enhancing the efficiency of security operations: With actionable insights, SOCs and IT teams can streamline their workflows, automate detection rules, and eliminate false positives.
Reducing incident response time: Intelligence-backed alerts enable faster investigation and containment of breaches, minimizing damage and downtime.
Supporting better executive decision-making: Leaders gain a clear understanding of threat trends and potential business impact, enabling informed investment and policy decisions.
Vulnerability Management: Enhances patch prioritization by linking vulnerabilities to known exploits in the wild. Instead of relying solely on CVSS scores, teams can patch based on active exploitation data derived from threat intelligence.
Fraud Prevention: Uncovers phishing campaigns, credential leaks, and impersonation attempts on the dark web and social media. This enables companies to detect fraud attempts before they impact users or brand reputation.
Executive Security Planning: Strategic threat intel provides decision-makers with a clear understanding of emerging risks and threat trends, helping them allocate budgets effectively, align with compliance standards, and shape long-term risk mitigation strategies.
Third-Party Risk Assessment: Identifies potential exposure through suppliers and partners by tracking breach disclosures, domain abuse, or leaked credentials associated with external vendors.
Security Tool Optimization: Feeds enriched threat intel into existing tools like SIEMs, firewalls, and SOAR platforms, enhancing detection rules, automation playbooks, and alert relevance.
Compliance and Reporting: Supports regulatory frameworks such as GDPR, NIS2, and ISO 27001 by documenting how organizations monitor and respond to cyber threats in a structured and measurable way.
Whether you’re a startup with limited resources or a large enterprise managing complex infrastructures, threat intelligence is your secret weapon to staying resilient, compliant, and ahead of attackers.
Who Needs Threat Intelligence in Today’s Cyber Landscape?
Threat intelligence isn’t just for large enterprises with deep pockets—it delivers measurable value across all organizational sizes and roles. Whether sourced from third-party providers or built through internal threat data and analysis, threat intelligence empowers teams to make informed, proactive decisions.
Here’s how it supports key roles within an organization:
Small and Medium Businesses (SMBs)
- Often lacking dedicated security teams, can use third-party threat intelligence to prioritize defenses, identify critical risks, and automate threat detection through managed solutions.
- Helps level the playing field by providing insights that would otherwise be out of reach.
Enterprises
- Large organizations benefit from deep visibility into global threat landscapes and tailored threat feeds.
- Enables efficient threat triage, resource allocation, and incident management at scale.
Managed Service Providers (MSPs)
MSPs are on the front lines of protecting multiple client environments across industries. By integrating threat intelligence into their security offerings, MSPs can:
- Detect and mitigate threats across customer infrastructures in real time
- Proactively adapt to emerging threats without waiting for vendor updates
- Deliver value-added services such as managed WAF, threat reporting, and compliance support.
Security Operations Center (SOC) Analysts
- Gain real-time alerts and contextual insights from integrated threat intelligence sources—both external and internal—to accelerate detection and minimize false positives.
- Improve decision-making by aligning alerts with known TTPs and threat actor profiles.
Threat Hunters and Malware Analysts
- Use indicators of compromise (IOCs), campaign data, and threat behavior analysis to proactively uncover hidden threats and reverse-engineer malware.
Incident Response (IR) Teams
- Threat intelligence helps connect the dots quickly during investigations -external intelligence speeds up actor attribution, while internal data provides context from the organization’s own environment.
- Accelerates containment by mapping observed activity to known threat actors or campaigns.
Intelligence Analysts
- Leverage threat feeds and reports to profile adversaries, track APT groups, and monitor geopolitical risks.
Executives and CISOs
- Strategic threat intel provides macro-level visibility into cyber risks affecting the business.
- Supports informed budgeting, risk management, and board-level reporting.
Third-Party Risk Managers
- Assess the risk posed by vendors, partners, or supply chain by monitoring leaked credentials, exposed assets, or past breaches.
Sector-Specific Organizations
- Industries like healthcare, finance, and government benefit from tailored intelligence that maps directly to regulatory frameworks, compliance requirements, and specific threat landscapes.
By delivering the right intelligence to the right people at the right time, threat intelligence empowers every layer of an organization to act decisively and with confidence.
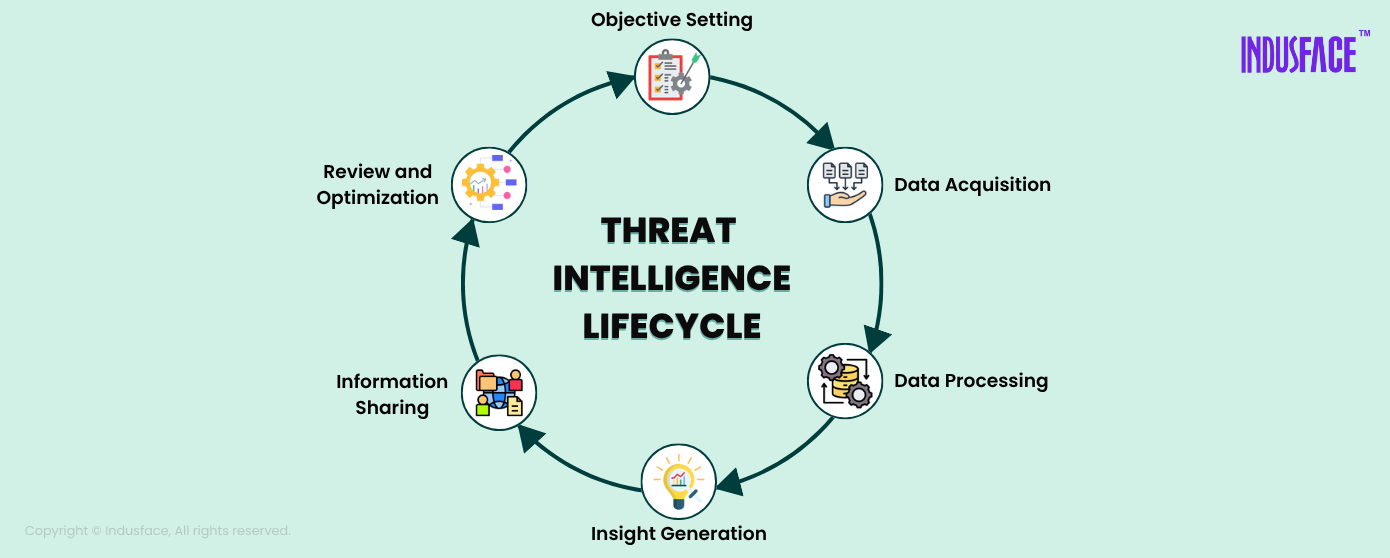
Key Stages of the Threat Intelligence Lifecycle
To deliver effective results, Threat Intelligence follows a structured cycle:
The effectiveness of any cyber threat intelligence program depends on a well-defined, continuous process. The Threat Intelligence Lifecycle outlines the essential stages that transform raw data into meaningful, actionable insights. This approach enables security teams to stay ahead of potential attacks by making faster, smarter decisions.
1. Objective Setting
Every successful threat intelligence program begins with clarity. In this stage, security leaders define the specific goals of their intelligence efforts, whether that’s monitoring ransomware trends, identifying remote code execution or protecting critical infrastructure. Clear objectives ensure the intelligence gathered is relevant and actionable for the organization.
2. Data Acquisition
With directions in place, the next step is to gather data from a wide range of internal and external sources. These can include system logs, vulnerability scanners, OSINT (open-source intelligence), dark web forums, threat data feeds, and industry-specific advisories. The more diverse and comprehensive the input, the more accurate the intelligence will be.
3. Data Processing
Raw data isn’t usable in its initial form. This phase involves filtering, normalizing, and organizing collected data. Unnecessary or duplicate information is discarded, while the remaining data is structured to highlight useful indicators such as suspicious IPs, file hashes, or anomalous patterns. Automation tools are often used here to improve speed and consistency.
4. Insight Generation
Once the data is cleaned, it’s analyzed to reveal hidden threats, behavioral trends, and potential vulnerabilities. This step helps build threat actor profiles, uncover attack chains, and predict how adversaries may attempt to compromise systems. Insights at this level form the backbone of proactive defense strategies.
5. Information Sharing
Intelligence must reach the right people at the right time. Security analysts might need real-time alerts, while CISOs may prefer executive-level summaries. Tailoring the delivery—whether through dashboards, reports, or integrations with SIEM/XDR platforms—ensures each stakeholder can act on the information effectively.
6. Review and Optimization
No process is complete without evaluation. This final phase involves reviewing what worked, what didn’t, and how to improve. Feedback from stakeholders helps refine data collection sources, adjust analysis criteria, and update goals—making the entire lifecycle more accurate and efficient with each iteration.
4 Types of Threat Intelligence and Their Use Cases
1. Tactical Threat Intelligence
- Focus: Based on indicators of compromise (IOCs) such as malicious IP addresses, URLs, domain names, and file hashes.
- Use Case: Typically used by SOC teams and automated security systems to identify and block known threats in real-time.
- Key Features: Highly granular and machine-readable; often integrated into SIEM, firewalls, and antivirus systems.
- Lifespan: Short-lived due to the dynamic nature of attacker infrastructure; requires constant updating.
Example: A list of malicious IPs associated with a phishing campaign targeting financial institutions. This data helps SOC analysts update firewall rules or block traffic in real time.
2. Operational Threat Intelligence
- Focus: On understanding the context behind attacks, including Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures (TTPs), threat actor motivations, and specific campaigns.
- Use Case: Empowers security analysts to conduct threat hunting, enhance detection rules, and build targeted mitigation strategies.
- Key Features: Includes insights into how specific attacks are executed and what tools are used, often tied to campaign-level intelligence.
- Lifespan: Moderate — more stable than tactical data, as TTPs don’t change frequently.
Example: A report detailing that a specific APT group is using spear-phishing emails with weaponized Excel attachments to deploy malware in banking systems. This helps incident responders prepare defenses and train staff.
3. Strategic Threat Intelligence
- Focus: Offers a high-level perspective on long-term risks, including geopolitical threats, industry trends, and evolving threat landscapes.
- Use Case: Used by CISOs, risk managers, and board-level executives to guide strategic planning, policy-making, and investment decisions.
- Key Features: Narrative-driven, often based on human analysis and reports from cybersecurity think tanks or intelligence firms.
- Lifespan: Long — remains relevant over months or even years due to its broad, macro-level scope.
Example: A quarterly report warning that ransomware attacks on healthcare systems are rising due to weak legacy infrastructure and high ransom payouts. This can influence budget decisions or trigger a board-level risk review.
4. Technical Threat Intelligence (Optional but Emerging)
- Focus: Technical signatures and artifacts such as malware hashes, exploit kits, and protocol anomalies.
- Use Case: Helps reverse engineers and malware analysts understand how specific exploits function.
- Key Features: Detailed, technical, and best suited for specialized teams such as malware research or red teams.
- Lifespan: Depends on malware evolution — can range from short to moderate.
Example: Example:
A newly discovered exploit code for a zero-day vulnerability in Apache servers being shared on dark web forums. This helps red teams and security vendors develop patches or detection signatures.
What to Look for in a Threat Intelligence Platform
Selecting the right Threat Intelligence Platform (TIP) is a crucial step in implementing a successful cyber threat intelligence program. A good TIP should not only centralize and manage threat data but also operationalize it across your existing security infrastructure. Here are key criteria to consider when evaluating options:
- Data Diversity: Ensure the platform supports aggregation of various data types — including malware signatures, open-source intelligence (OSINT), dark web insights, telemetry from security tools, and human-sourced intelligence. The broader the input sources, the more comprehensive the threat picture.
- Integration Support: Look for seamless integrations with your existing security stack. This includes support for STIX/TAXII standards, and compatibility with SIEM, SOAR, XDR, EDR, and firewalls. Efficient ingestion and export of threat intel boosts operational value.
- Customization: A robust TIP should offer customizable threat scoring, filtering rules, dashboard views, and alerting workflows. This flexibility helps tailor intel output to the needs of different teams — from analysts to executives.
- Automation and AI/ML: Automation is key to reducing analyst fatigue. Platforms with AI-driven enrichment, automated IOC correlation, and threat prioritization help you cut through noise and focus on the highest risks first.
- User Experience and Collaboration: Opt for platforms featuring user-friendly interfaces, collaborative workbenches, and role-based access control (RBAC) support. These features empower cross-functional teams to work together more effectively.
- Scalability and Performance: Ensure the platform can scale with your organization’s growth and handle large volumes of data without performance degradation.
- Vendor Support and Community: A responsive support team, strong documentation, and active user community are critical. Look for platforms with threat-sharing communities or ISAC integrations to enhance collective intelligence.
Ultimately, the best TIP is the one that aligns with your maturity level, operational needs, and strategic goals — enabling you to turn threat intelligence into a competitive security advantage.
AppTrana’s Advanced Threat Detection Powered by Threat Intelligence
AppTrana WAAP (Web Application and API Protection) integrates threat intelligence at every layer to provide proactive, adaptive, and context-aware protection. By combining global threat feeds, customer-specific data, behavioral analysis, and security expert insights, AppTrana ensures real-time defense against both known and emerging threats.
Here’s how it works:
- Real-time threat feeds: AppTrana integrates curated global threat intelligence from trusted external sources to stay ahead of evolving threats, including emerging CVEs, botnets, and malicious IPs.
- Behavioral analytics and telemetry: It continuously analyzes traffic patterns and anomalies across thousands of protected applications, generating proprietary threat intelligence that helps detect zero-day attacks and complex evasive threats.
- Bot intelligence: AppTrana combines threat data with bot signature libraries and behavioral cues to accurately identify and mitigate malicious bots without affecting legitimate traffic.
- TTP correlation: Known tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) from threat actors are mapped to observed activity, enabling precise rule tuning and risk-based mitigation.
- CVE monitoring and exploit analysis: The security team actively tracks CVEs exploited in the wild and monitors related exploit activity. They evaluate exploitability in real time and rapidly builds scanning plugins for newly emerging threats. This enables faster identification and response to vulnerabilities, ensuring customers stay ahead of evolving risks. For detailed coverage on latest CVEs and how AppTrana addresses them, visit our security bulletin page.
- Customized protection: Based on live threat intelligence, AppTrana dynamically adjusts its security posture—applying virtual patches, deploying custom rules, and enforcing granular rate limits—to guard against targeted and evolving attacks.


