DNS (Domain Name System) is a vital internet service that translates human-readable domain names into unique IP addresses, enabling access to websites. It supports essential services like chat, email, and social networks by continuously converting IP addresses into hostnames.
Given its significance, DNS is a prime target for attackers. Many organizations overlook this component when securing their infrastructure, leaving it outdated or improperly protected. As a result, DNS attacks are on the rise.
In this article, we will explore DNS flood attacks, a common type of DNS-based attack that can impact your organization.
What is DNS Flood?
Like other Internet resources, DNS is also highly prone to DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) attacks.
DNS flooding is a symmetric DDoS attack. When a DNS server is flooded in a DDoS attack, the attack attempts to exhaust server resources with floods of IP addresses. The main goal of the DNS flood DDoS attack is to overload the victim server and make it not able to serve DNS requests since the available resources are affected by the hosted DNS zones.
How Does DNS Flood Attack Works?
A DNS flood attack is a type of Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack that targets DNS servers by overwhelming them with an excessive volume of traffic. Attackers typically begin by setting up a botnet, a network of compromised devices that can be controlled remotely, or they might use a single device with multiple IP addresses to generate traffic. Once the target—a specific DNS server, either public or belonging to an organization—is selected, the attacker sends a flood of DNS requests.
These requests can be legitimate but are sent in such high quantities that they overwhelm the server’s resources, such as CPU, memory, or network bandwidth. As a result, the DNS server becomes slow or unresponsive, leading to a denial of service for legitimate users. This disruption can prevent users from accessing websites, causing significant business interruptions, loss of revenue, and potential damage to an organization’s reputation.
To mitigate such attacks, organizations can implement strategies like using DDoS protection services, employing DNS firewalls, and ensuring their server configurations are robust.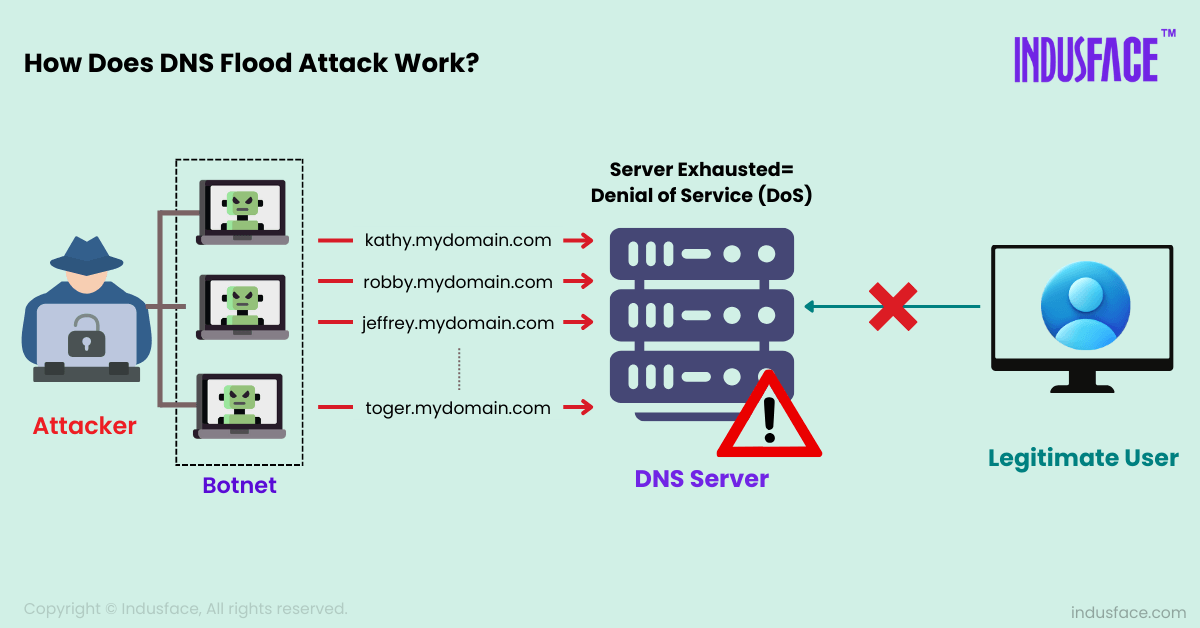
DNS NXDOMAIN Attack
The DNS NXDOMAIN attack is another common type of DNS Flood attack, which involves flooding a target DNS server with requests for non-existent domain names, which results in an NXDOMAIN (Non-Existent Domain) response.
In this attack, the attacker generates a high volume of queries for domains that do not exist, overwhelming the DNS server and consuming its resources.
DNS Flood Attack Mitigation Approaches
Keep Your Resolver Private – Make sure your own resolver is not open to external users. It is recommended to restrict its usage only to your network users to prevent its cache from being contaminated by attackers outside your company.
Effective Patch Management Solution – Cybercriminals exploit loopholes and vulnerabilities in software. Therefore, it is vital to apply patches as soon as possible. Keeping name servers patched and up to date can prevent them from being exploited through known vulnerabilities.
Implement a DNS Firewall – A DNS firewall adds an extra layer of protection by filtering out malicious traffic before it reaches your DNS servers. This helps in blocking harmful requests and preventing potential exploitation from DNS-based attacks.
Use A Dedicated DNS Server –Small organizations often host their DNS servers alongside their application servers due to cost constraints. However, this practice increases the risk of DNS flood DDoS attacks. It is advisable to run your DNS services on a dedicated server to enhance security and reliability.
Conduct a DNS Audit – Over time, organizations often overlook their old subdomains, some of which may be running outdated software or be vulnerable to exploitation. Regularly auditing your DNS zones can provide valuable insights into DNS-related vulnerabilities, helping you identify and address areas that need attention.
Use DDoS Mitigation Solution – DNS servers are vulnerable to DDoS attacks, which can render your services inaccessible and disrupt business operations. To prevent DNS DDoS flooding, consider using DDoS mitigation solutions. For example, AppTrana’s fully managed DDoS protection service can help block unwanted traffic and keep your DNS services operational.



