Magento Patching Without Panic: How Agencies Protect Stores While Updates Catch Up
If you run a Magento agency, you know the feeling: it is 4:00 PM on a Friday, and a critical vulnerability like SessionReaper drops. You are now stuck between two impossible choices. Do you rush an emergency patch and risk breaking your checkout flow right before the weekend? Or do you wait for a safe testing window and pray you don’t become a statistic?
For 62% of store owners, the choice was “wait and pray” and it failed. Weeks after the fix for SessionReaper was released, 62% of Magento stores remained vulnerable, not because agencies were lazy, but because applying a patch in Adobe Commerce is not a simple “click update.” It is a complex change event that requires staging, testing, and downtime. Yet attackers began weaponizing the exploit within just 5 days of disclosure.
This is where “Panic-Free Patching” changes the game.
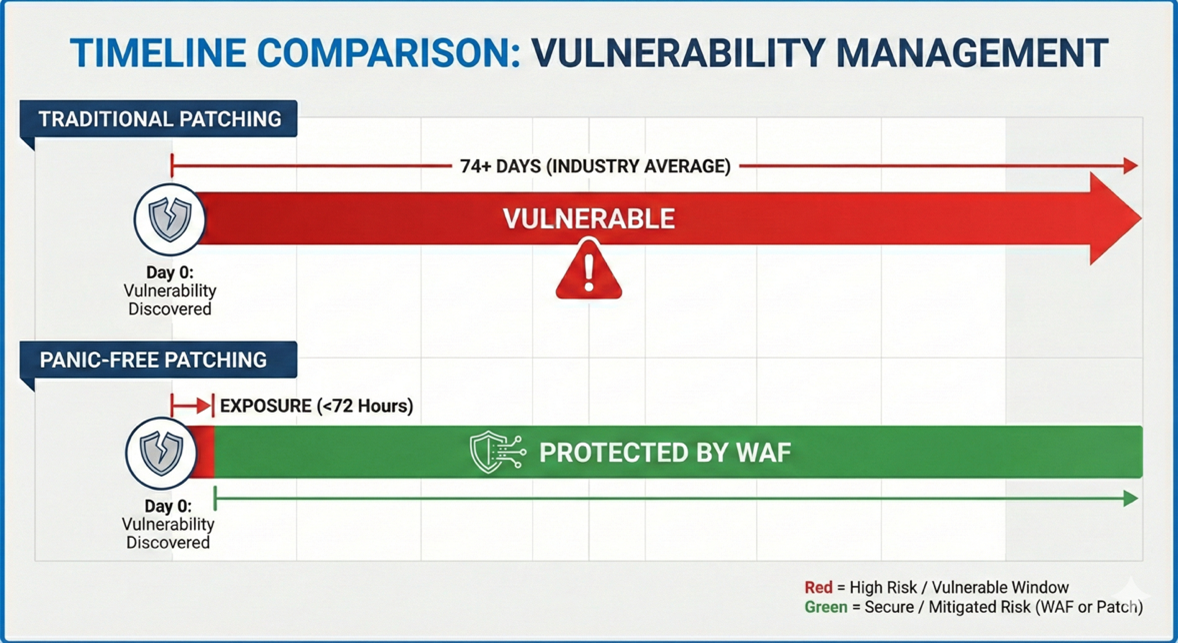
For readers new to this series, Panic-Free Patching is the strategy of using a Web Application Firewall (WAF) to apply a “virtual patch” at the edge immediately. This insurance policy blocks the attack vector instantly, allowing you to reduce the risk now and schedule the complex code integration safely later.
To understand the full agency framework behind this strategy, and how to sell it to clients, read our foundational guide on [Panic-Free Patching: The Insurance Policy That Buys You Time].
Why Magento Patches are Notoriously Difficult to Apply
If you have ever had a client ask, “Why does this security update cost three hours of billable time when my WordPress plugin updates automatically?” you know the frustration.
The uncomfortable truth is that in the Adobe Commerce ecosystem, a “patch” is not a maintenance task; it is a deployment event.
1. The “Staging Tax” is non-negotiable
Unlike simpler CMS platforms where updates are often “hot-swappable,” Adobe explicitly warns against applying patches directly to production. The interdependencies between core files, third-party extensions, and custom themes mean that even a minor security fix can trigger a fatal error in the checkout flow.
To stay compliant with Adobe’s own best practices, every patch requires a rigid sequence: full backup, deployment to Integration/Staging, regression testing, and finally, a scheduled release to Production. This, in essence, is a full release cycle.
2. The hidden cost of “Patch Sprawl”
For an agency managing 20 or 50 installs, the complexity multiplies. Adobe acknowledges that applying individual security hotfixes manually contributes to “patch sprawl”, a state where your codebase becomes a patchwork of individual fixes that diverge from the core.
This creates technical debt. Every hotfix you apply today is a potential conflict you will have to resolve during the next major version upgrade. The more you rush to patch code manually, the harder you make your future work.
The Agency Owner’s Takeaway: This creates a fundamental tension in your operations. “Patch Fast” protects you from hackers, but “Patch Safely” protects you from broken sites.
In a manual workflow, you cannot do both. If you rush, you risk the site. If you test properly, you risk the hack. This is exactly why you need a layer: it buys you the time to resolve that tension without compromising either security or stability.
The Conflict: Attack Speed vs. Patch Speed
Attackers weaponize exploits within 48 hours. A safe Magento deployment cycle requires weeks. This temporal mismatch creates the risk window. The only way to close this window without compromising stability is to decouple “protection” from “patching.”
The Protocol: How to Match the Attacker’s Speed
This process ensures defenses operate at the speed of the threat, regardless of the development timeline.
- The Foundation: The WAF must operate inBlock Modeto filter requests in real-time. The origin server must enforce Origin Protection, accepting traffic exclusively from the WAF’s IP ranges. This configuration guarantees immediate inspection of every request and prevents bypass attempts.
- The First Check: Core Rule Validation Speed often comes from existing capabilities. Many “zero-day” exploits utilize known vectors like The vendor SOC immediately validates the new threat against the active Core Rule Set. If the existing policy blocks the payload, protection is already active. This step provides instant confirmation. With the shield confirmed, the development team schedules the official patch during the standard maintenance window.
- The Gap Fill: Custom Virtual Patchingif the vulnerability utilizes a novel vector, the SOC drafts a custom virtual patch. This rule targets the specific exploit signature. The vendor SOC applies this rule to the WAF immediately. This action neutralizes the threat in real-time, allowing the development team to proceed with the standard, safe release cycle.
SessionReaper: The Real-World Proof of “Patching Is Hard”
The SessionReaper vulnerability serves as the perfect case study for why manual patching often fails to beat the attacker’s clock. It demonstrates exactly how a technical vulnerability transforms into an operational crisis for an agency.
The industry tracks SessionReaper as CVE-2025-54236. Security researchers define it as an improper input validation vulnerability within the Adobe Commerce framework. Attackers exploit this weakness to manipulate session data, allowing for unauthorized session takeover. Publicly available Proof of Concepts (PoCs) demonstrate that sophisticated actors use this entry point to achieve Remote Code Execution (RCE) without authentication. This effectively hands the keys to the store over to the attacker.
Why agencies must care
This vulnerability transcends simple technical debt. It strikes directly at the trust architecture of an eCommerce business.
- Checkout & Account Trust: An exploit allows attackers to hijack active user sessions. This means a hacker enters a legitimate customer’s account during checkout, accessing saved payment methods and personal data.
- Fraud Liability: Session hijacking enables automated fraud at scale. Attackers place fraudulent orders using compromised accounts, creating immediate chargeback liabilities for the merchant.
- Regulatory Signal: The U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) added this CVE to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV). This designation confirms that active exploitation is happening in the wild, removing any “wait and see” optionality for compliance-focused brands.
The gap between the “fix” and the “threat” illustrates the agency’s dilemma.
- Adobe Discloses Patch: September 9, 2025
- Public PoC Released: October 22, 2025
- Active Exploitation Begins: Late October 2025 (Immediately following PoC)
This timeline reveals the “safe patching window” was roughly six weeks. Once the PoC dropped, that window closed instantly. Agencies relying solely on manual code deployment lost the race the moment the exploit code became public. Virtual patching keeps that window open indefinitely.
The Who Does the Virtual Patching Question: Magento Economics 101
Writing a WAF rule is the easy part. The actual labor lies in False Positive Testing.
- The Hidden Burden of QA: A Magento store is a complex web of SOAP APIs, ERP integrations, and payment gateway webhooks. A security rule that looks correct on paper often conflicts with legitimate traffic patterns. For example, a standard SQL injection filter might inadvertently block a legitimate SKU search or a saved address containing special characters.
- The Economic Opportunity Cost:Validating a virtual patch requires rigorous testing. A developer must simulate traffic, analyze log files, and fine-tune the rule to ensure it permits all valid customer journeys. This process takes hours. Every hour a certified Magento developer spends tailing access logs to verify a false positive is an hour lost on billable feature development.
- The Solution: Partnering with a Managed WAF provider like AppTrana transfers this validation burden off your team. The SOC handles the rule creationandthe rigorous testing required to verify it. They assume the responsibility for accuracy, standing behind a Zero False Positives guarantee. Your team focuses on the store; the SOC guarantees the shield.
The Magento SOP: Solving the “Code Freeze” Dilemma
The most critical use case for virtual patching in Magento occurs when you cannot deploy code at all.
- The Code Freeze Reality: High-volume merchants enforce strict code freezes, particularly during Q4 (Black Friday/Cyber Monday). During these windows, the deployment pipeline is locked to ensure stability.
- The Security Conflict: Vulnerabilities ignore business calendars. If a Critical CVE drops on November 25th, the standard patching workflow forces a choice between violating the freeze (risking stability) or accepting the risk (risking a breach).
- The Virtual Patching Exception: Virtual patching provides the compliant solution. The SOC applies the rule at the edge. The application code remains untouched. The freeze remains respected. The site remains secure. This specific capability allows the agency to uphold its stability guarantees without compromising its security posture.
For a detailed breakdown of how to structure your agency’s security retainer and pricing models, read our full guide on [Panic-Free Patching for Agencies].
The Partner Model: You Sell, We Run
AppTrana is built to function as the specialized security division of your agency. This partnership model allows you to deliver enterprise-grade virtual patching without the overhead of building an internal security operations center.
- The Division of Labor: We operate on a “You Sell, We Run” basis. Your agency retains full ownership of the client relationship, the contract, and the billing. The AppTrana SOC operates in the background to execute the technical defense. Our engineers handle the rule creation, the false positive tuning, and the continuous monitoring required to keep the WAF effective.
- Scalable Expertise: This model grants you immediate access to a team of security experts who understand the nuances of Adobe Commerce. You leverage our infrastructure to deliver a “Managed Security” premium tier today. This approach secures your clients’ revenue and your agency’s margins simultaneously.
Next Steps: Stop the Panic
You can transform vulnerability response from a crisis into a routine maintenance task.
- Pilot on Your Toughest Site: Select one of your most complex Magento installs. An app with custom checkouts and heavy API traffic. Deploy AppTrana and let the SOC prove the “Zero False Positive” guarantee in a live environment.
- Update Your Care Plans: Move “Virtual Patching” from an ad-hoc emergency cost to a recurring value driver. Bundle this protection into your top-tier maintenance package to increase monthly recurring revenue.
Partner with us today. Talk to sales.
Stay tuned for more relevant and interesting security articles. Follow Indusface on Facebook, Twitter, and LinkedIn.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Two prerequisites: (1) traffic must be forced through the WAF, and (2) the WAF must be in enforcement (block mode), not just observing.
Operationally, it is designed to be a five-minute onboarding process. The agency makes a DNS change, and AppTrana’s default state is block mode from Day 1.
To avoid back-and-forth, send a minimum context bundle: store URL, time window with timezone, affected path (checkout, login, admin, APIs), any signal you have (blocked screenshot, IP, request ID), and business impact.
Treat Magento like an eCommerce system, not a brochure site. Pre-map critical paths and “known-good” sources like payment gateway callbacks, SSO, partner IPs, monitors, and key APIs before go-live.
It does not have to. Standardize the agency-side inputs (critical path mapping, known-goods list, integration audit) so the SOC can operate consistently across stores.
That is exactly where virtual patching shines. Protections are applied at the edge without touching application code, so you can respect a freeze while still reducing exposure.
Keep it until your permanent fix is deployed and stable. There is no impact on site performance even if you let it be as is.
Use an executive-ready line that translates invisible work into outcomes, then back it with a technical appendix if needed. This lets you report “we reduced risk immediately while scheduling safe fixes” without exposing sensitive details.


 January 23, 2026
January 23, 2026






