What are SSL Stripping Attacks and How to Prevent Them?
What is SSL Stripping?
An SSL stripping attack is a type of man-in-the-middle attack that downgrades a secure HTTPS connection to an insecure HTTP connection. It is also known as SSL Downgrade Attack.
This attack is designed to intercept and manipulate data exchanged between a user and a website, despite the user’s intention to use a secure HTTPS connection.
How Does SSL Stripping Attack Work?
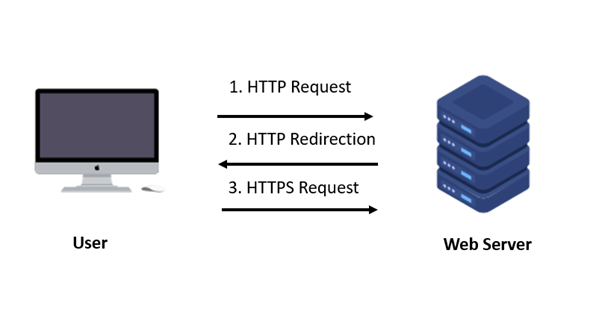
When a user tries to visit a website, their browser starts with an insecure HTTP connection. This initial HTTP request is made to the website to verify if HTTPS (HTTP Secure) is supported.
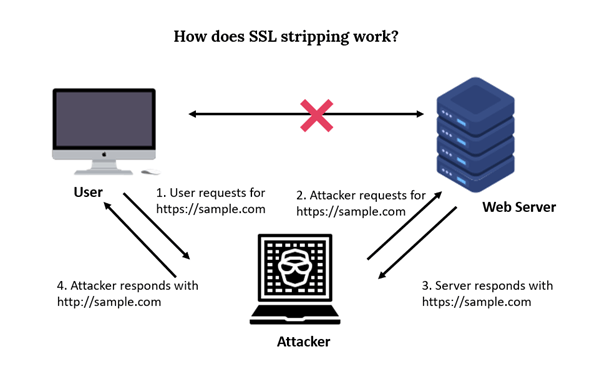
The attacker intercepts the connection between the user and the website. This can be done through various methods such as setting up a fake Wi-Fi network, using ARP spoofing, or manipulating DNS settings.
As the user sends their HTTP request, the attacker intercepts it.
The attacker establishes a secure HTTPS connection with the website, posing as the legitimate user. At the same time, the attacker sets up an insecure HTTP connection with the user.
When the website responds, it sends the attacker data over the HTTPS connection. The attacker then forwards this data to the user over the HTTP connection.
Normally, the browser would upgrade the connection to HTTPS once it receives a redirection from HTTP. In an SSL stripping attack, the attacker prevents this redirection from happening.
The attacker may remove or alter the redirection to HTTPS, ensuring that the user’s connection remains unencrypted.
Since the attacker is in the middle, they can monitor, capture, and alter the data exchanged between the user and the website.
The attacker sees all data sent by the user, such as login credentials, personal information, and any sensitive communications. They can also modify the responses from the website before they reach the user.
With the plaintext data in hand, the attacker can modify the content sent to and received from the user. This can include altering web pages, injecting malicious content, or redirecting users to phishing sites.
Reasons Behind Successful SSL Stripping Attack
Public Hotspots: Attackers often set up fake public Wi-Fi networks with names similar to legitimate ones. Users connecting to these hotspots are at risk of SSL stripping attacks.
Incomplete URLs: Users frequently enter only the domain name without specifying https://. This allows attackers to present HTTP links and intercept the communication.
Inconsistent HTTPS Use: Some websites use HTTPS only for sensitive pages like login forms while serving other pages over HTTP. This leaves those pages exposed to attacks.
Lack of Detection: Both users and servers typically cannot detect SSL stripping attacks. They assume data is secure and being exchanged with a legitimate partner.
Limited Visibility: SSL stripping attacks are hard to detect and only show up in rare cases through specific design or technical flaws. There are few visible signs that the connection is not secure.
What are the Risks of SSL Stripping Attacks?
SSL stripping attacks can lead to several serious risks:
Data Exposure: Sensitive information, such as login credentials, personal details, and financial data, is transmitted in plaintext and can be intercepted by attackers.
Identity Theft: Attackers can capture personal information and credentials, leading to identity theft and unauthorized access to accounts.
Account Compromise: Stolen login credentials can be used to gain unauthorized access to user accounts, potentially leading to fraud or further attacks.
Data Manipulation: Attackers can alter the data being transmitted, potentially injecting malicious content or altering responses from the website.
Phishing and Fraud: Attackers can redirect users to fake websites or phishing pages to steal additional information or trick users into revealing more data.
Loss of Trust: Successful attacks can damage an organization’s reputation, leading to a loss of user trust and confidence in its security measures.
Compliance Violations: Exposure of sensitive data may lead to violations of data protection regulations, resulting in legal consequences and financial penalties.
Undetected Attacks: Since SSL stripping attacks are often difficult to detect, attackers can operate without being noticed for extended periods, increasing the potential damage.
How to Detect SSL Stripping Attacks?
Detecting SSL stripping attacks can be challenging, but here are some signs and methods to help identify such attacks:
Mixed Content Warnings: Browsers may display warnings when a webpage contains both HTTP and HTTPS content. If you see such warnings, it could be a sign of SSL stripping.
Unusual Connection Behavior: If your browser shows a connection as “not secure” despite expecting HTTPS, or if you are redirected to HTTP without clear reason, it may indicate an SSL stripping attack.
Certificate Warnings: Pay attention to any certificate errors or warnings. Attackers might not be able to fully mimic the original site’s SSL certificate, leading to noticeable discrepancies.
Inconsistent URL Schemes: If you see URLs that should be HTTPS but are loading as HTTP, it may suggest that SSL/TLS has been stripped.
Unencrypted Communication: Use tools like browser developer tools or network analysis tools to verify that sensitive data is being transmitted in plaintext rather than encrypted.
How to Prevent SSL Stripping Attacks?
- Implement HSTS (HTTP Strict Transport Security) – Configure your web server to use HSTS, which forces browsers to only connect via HTTPS. This prevents attackers from downgrading the connection to HTTP.
- Regularly Update SSL/TLS Certificates – Ensure SSL/TLS certificates are current, valid, and correctly configured. Use certificate pinning where possible to prevent interception. It is recommended to hire Certificate Management System like Entrust CMS offered by Indusface to monitor and manage certificate lifecycle, public key infrastructure, and certificate validity to prevent bad actors from misusing the certificate.
- Use HTTPS for All Pages – Ensure that all pages and resources on your site are served over HTTPS. Don’t rely on HTTPS only for sensitive pages like login forms.
- Enforce HTTPS Redirection – Set up server-side redirects to automatically send users from HTTP to HTTPS. This ensures that any HTTP requests are upgraded to a secure connection.
- Educate Users – Inform users to look for “https://” in the URL and to be cautious of any warnings about insecure connections or certificate issues.
- Secure Public Wi-Fi Connections – Encourage users to use Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) when connecting to public Wi-Fi networks to protect their data from being intercepted.
- Monitor and Audit Security – Perform regular security audits and vulnerability assessments to identify and address any potential weaknesses in your HTTPS implementation.
- Check for Mixed Content – Use tools to scan for mixed content issues where both HTTP and HTTPS resources are loaded on the same page. Ensure all resources are served securely.
By implementing these measures, you can significantly reduce the risk of SSL stripping attacks and enhance the overall security of your web communications.
Stay tuned for more relevant and interesting security articles. Follow Indusface on Facebook, Twitter, and LinkedIn.


 June 23, 2022
June 23, 2022






