CVE-2025-3248: Critical Langflow Unauthenticated Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
A critical vulnerability in Langflow’s code validation mechanism allows unauthenticated attackers to execute arbitrary Python code on exposed systems. Tracked as CVE-2025-3248, the vulnerability resides in a publicly accessible API endpoint and affects all Langflow versions prior to 1.3.0. Active exploitation has been confirmed, with attackers using the vulnerability to deploy malware and onboard compromised systems into botnet infrastructure.
Because exploitation requires no authentication and provides direct code execution, internet-facing Langflow deployments running affected versions face immediate and severe risk.
Risk Analysis: CVE-2025-3248
Severity: CRITICAL
CVSS v3.1 Base Score: 9.8 (CRITICAL)
Vector: CVSS:3.1/AV:N/AC:L/PR:N/UI:N/S:U/C:H/I:H/A:H
Exploit available in public: Yes
Exploit complexity: Low
Affected Product: Langflow
Affected Versions: All versions prior to 1.3.0
Vulnerable Endpoint: /api/v1/validate/code
CVE-2025-3248 represents an unauthenticated remote code execution condition exposed through a network-accessible Langflow API endpoint. The risk is amplified by the absence of authentication controls and the vulnerability’s complete impact across confidentiality, integrity, and availability. Public exploit availability and low exploitation complexity make it well suited for automated attacks, particularly against unprotected, internet-facing Langflow deployments.
Root Cause Behind CVE-2025-3248 in Langflow
CVE-2025-3248 originates from Langflow’s implementation of server-side validation for user-submitted Python code. The /api/v1/validate/code endpoint was intended to validate code structure but instead executes the submitted input as part of the validation process, rather than performing static analysis.
In practice, the endpoint:
- Parses the submitted code usingparse()
- Compiles it usingcompile()
- Executes it using Python’sexec() function
In Python, certain constructs, specifically function decorators and default argument values, are evaluated immediately when a function is defined. Attackers exploit this behavior by embedding malicious logic into these constructs, causing code execution as soon as the validation request is processed.
Because the endpoint:
- Is accessible without authentication
- Lacks authorization checks
- Does not apply sandboxing or execution controls
the validation mechanism effectively functions as an unauthenticated remote command execution interface.
How CVE-2025-3248 Is Exploited in Real-World Attacks
Exploitation of CVE-2025-3248 is simple and requires no authentication or user interaction. Attackers first identify internet-exposed Langflow instances through automated scanning or search engines.
A malicious Python payload is then embedded into function decorators or default parameter values, which constructs that Python evaluates during function definition, and sent to the /api/v1/validate/code endpoint in a POST request. When Langflow processes the request, it parses and executes the embedded code as part of validation, resulting in immediate server-side execution.
Once exploited, attackers can run system commands, download additional payloads, establish persistence, or deploy malware and botnet components. In many cases, the API returns a normal response, helping mask the attack and making detection more difficult at the application layer.
Impact of CVE-2025-3248 on Langflow Systems
Successful exploitation of CVE-2025-3248 results in immediate and full compromise of the affected system. Because the vulnerability allows unauthenticated remote code execution, attackers gain direct control over the Langflow host with minimal effort.
From a security standpoint, attackers can access sensitive environment variables, credentials, configuration files, and application data, undermining confidentiality. Integrity is impacted as arbitrary commands enable modification of application logic, system binaries, or configurations. Availability is also at risk, as compromised systems can be destabilized or repurposed for denial-of-service attacks.
The operational impact is equally severe. Affected hosts can be fully taken over and abused for malicious campaigns, leading to service disruption, reputational damage, and increased regulatory or compliance exposure. The lack of authentication makes large-scale exploitation practical, particularly for internet-facing Langflow deployments.
CVE-2025-3248 – Mitigation and Remediation Guidance
Organizations running affected Langflow versions should take the following actions to reduce exposure and prevent exploitation
Immediate Remediation Steps:
- Upgrade Langflow to version 1.3.0 or later, which introduces mandatory authentication on the vulnerable endpoint.
- Restrict network exposure to /api/v1/validate/code using firewalls, security groups, or IP allow lists.
- Ensure authentication and authorization are enforced for all sensitive API endpoints.
Additional Hardening Measures
- Review API access patterns and disable unused endpoints.
- Monitor logs for unusual or repeated validation requests.
- Implement rate limiting to reduce automated probing and exploitation attempts.
How AppTrana WAAP Helps Mitigate CVE-2025-3248
AppTrana WAAP has provided protection against exploitation attempts targeting CVE-2025-3248 from day zero. The platform applies built-in inspection and enforcement controls to identify and block malicious requests abusing vulnerable application behavior.
By stopping exploitation attempts before they reach the application layer, AppTrana helps reduce the risk of unauthorized code execution and follow-on compromise during active exploitation and patching windows. This approach ensures continuous protection while remediation efforts are underway, without exposing implementation details that could be abused.
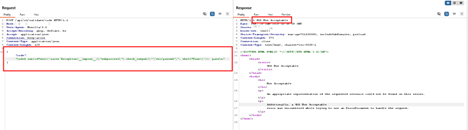
Screenshot showing malicious validation payloads associated with CVE-2025-3248, detected and blocked by AppTrana WAAP.
Stay tuned for more relevant and interesting security articles. Follow Indusface on Facebook, Twitter, and LinkedIn.

 January 23, 2026
January 23, 2026



