CVE-2026-22610: Angular Template Compiler XSS Vulnerability Enabling Client-Side Script Execution
Angular applications often rely on built-in protections to handle user input safely. However, a recently disclosed vulnerability shows how gaps in this trust can lead to client-side attacks when input is not properly handled.
The vulnerability lies in Angular’s template sanitization logic, where improper handling of SVG <script> elements during template compilation allows attackers to execute arbitrary JavaScript in a user’s browser. Tracked as CVE-2026-22610, the vulnerability affects Angular’s Template Compiler and enables cross-site scripting through unsafe attribute bindings.
While the vulnerability does not lead to server-side compromise, successful exploitation allows client-side code execution that can expose user sessions, sensitive data, and application state, weakening trust boundaries in affected Angular applications.
Risk Analysis: CVE-2026-22610
Severity : HIGH
CVSS v4.0: Base Score : 8.5
Vector: CVSS:4.0/AV:N/AC:L/AT:N/PR:L/UI:A/VC:H/VI:H/VA:H/SC:N/SI:N/SA:N
Exploit available in public : No
Exploit complexity : Low
The risk associated with CVE-2026-22610 is driven by the execution of attacker-controlled JavaScript within the browser context of an Angular application. Successful exploitation can expose user sessions, leak sensitive client-side data, and allow attackers to perform unauthorized actions on behalf of legitimate users.
Root Cause Behind CVE-2026-22610 in Angular
Angular enforces client-side security by assigning template bindings to predefined security contexts, including HTML, URL, and Resource URL. Attributes that can load executable resources, such as script sources, are expected to be classified under the Resource URL context so that strict sanitization is applied.
CVE-2026-22610 is caused by a gap in this classification logic within Angular’s Template Compiler when handling SVG <script> elements. For standard HTML <script> tags, the src attribute is correctly recognized as a Resource URL and is subject to appropriate sanitization. However, SVG <script> elements use the href or xlink:href attributes instead of src.
Angular’s compiler does not classify these SVG-specific attributes as Resource URL contexts. As a result, values bound to href or xlink:href on SVG <script> elements are not subjected to Resource URL sanitization and are instead treated as non-executable string values.
When template bindings assign user-controlled input to these attributes, this misclassification allows script sources to bypass Angular’s intended sanitization controls, enabling execution of attacker-supplied JavaScript within the browser context.
How CVE-2026-22610 Can Be Exploited
Exploitation of CVE-2026-22610 depends on specific application behavior and is not automatically triggered. A vulnerable scenario requires that the application renders SVG <script> elements and processes user-controlled values during page load.
When these conditions are met, an attacker can supply malicious values, such as data:text/javascript URLs or references to external scripts, which execute directly in the victim’s browser. The code runs within the application’s security context, allowing the attacker to act as the authenticated user.
Successful exploitation enables session token and local storage theft, unauthorized actions performed on behalf of the victim, and data exfiltration from rendered application content. While the vulnerability does not grant server-side access, it significantly weakens client-side trust boundaries and can be chained with other browser-based vulnerabilities, leading to broader security and compliance impact.
Mitigation and Remediation Guidance
The most effective remediation for CVE-2026-22610 is to upgrade Angular to a patched release where the sanitization logic correctly classifies SVG <script> attributes as Resource URLs. Fixed versions include:
- 2.18
- 3.16
- 0.7
- 1.0-rc.0
Applications running Angular versions prior to v19 are end-of-life and will not receive security fixes, increasing long-term exposure.
If an immediate upgrade is not feasible, interim mitigations should focus on eliminating unsafe template patterns:
- Avoid dynamic bindings on SVG<script> elements entirely.
- Do not bind untrusted or user-controlled input tohref or xlink:href
- Enforce strict allowlists for any script-related URLs before values are passed into templates.
It is important to note that this vulnerability cannot be reliably mitigated at runtime once unsafe bindings exist. Correcting template logic and upgrading to a fixed Angular version are essential to fully eliminate the risk.
Why CVE-2026-22610 Matters
CVE-2026-22610 highlights how framework-level sanitization gaps, rather than developer error, can introduce exploitable security weaknesses. SVG handling remains a high-risk edge case in modern front-end frameworks, and subtle context misclassification can have serious consequences.
Despite being a client-side vulnerability, the impact is substantial. This vulnerability is particularly relevant for applications handling sensitive user data or long-lived authenticated sessions.
For organizations relying on Angular, especially in long-lived enterprise deployments, this vulnerability reinforces the need for proactive framework updates, careful template design, and continuous security review.
How AppTrana Helps Mitigate CVE-2026-22610
AppTrana WAAP helps reduce the risk associated with CVE-2026-22610 by providing an additional, application-layer security control for Angular applications. The platform applies built-in protection mechanisms to limit exposure to client-side script injection risks without requiring application changes or custom rule configuration.
AppTrana has provided coverage for exploitation attempts related to this vulnerability from day zero, helping maintain protection during patching and remediation efforts. This defense-in-depth approach is particularly valuable for applications that handle sensitive user interactions.
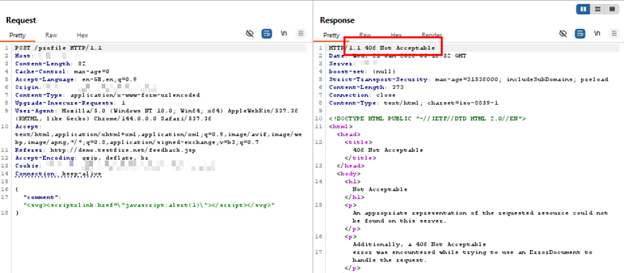
Screenshot showing client-side exploitation attempts associated with CVE-2026-22610, detected and blocked by AppTrana WAAP.
Stay tuned for more relevant and interesting security articles. Follow Indusface on Facebook, Twitter, and LinkedIn.

 January 28, 2026
January 28, 2026



